Layered Architecture Pattern
Introduction
Enterprise software systems needs to build assuming that every functional requirement can be varied over the time. Scope creeps and requirement changes are pretty common in enterprise software systems. The business leaders always wants to put the best piece of functionality in front of their customers no matter what is going on down under.
Software systems are not started in a manner that they are well thought out at the beginning. The reason was that, those systems had limited capabilities and many other challenges like hardware capabilities, sofrware capabilities, cost. It is understandable that these systems are not in the same way that enterprise architects or business leaders wants it to be. It is the challenge ahead of a solutions architect to build a modular system which can be used for next 10 years without much hassle.
Requirement identification
Enterprise software systems are typically running down under and most of the end users like employees, partners and customers think that as a luxury in their hands and expect it to run 24x7x365. Users do not care the actual information coming in and how they are coming in. But the system designers have to think about a lot of factors when designing these systems. Here are some of the basic requirements which needs to be addressed with an enterprise software system.
- Availability
- Performance
- Security
- Monitoring
- Quality of information
Layered architecture
Instead of building a one large monolith which has all these capabilities, the solutions architects over the time has identified that building a system with a layered architecture provides more flexibility when it comes to adding more and more features based on the business requirements. It also allows each layers to be independently scale, update and have their own technology which is best suited for the task. Building a layered architecture requires the designers of this architecture to understand what each layer does and how these layers are interact with each other so that those layers are loosely coupled.
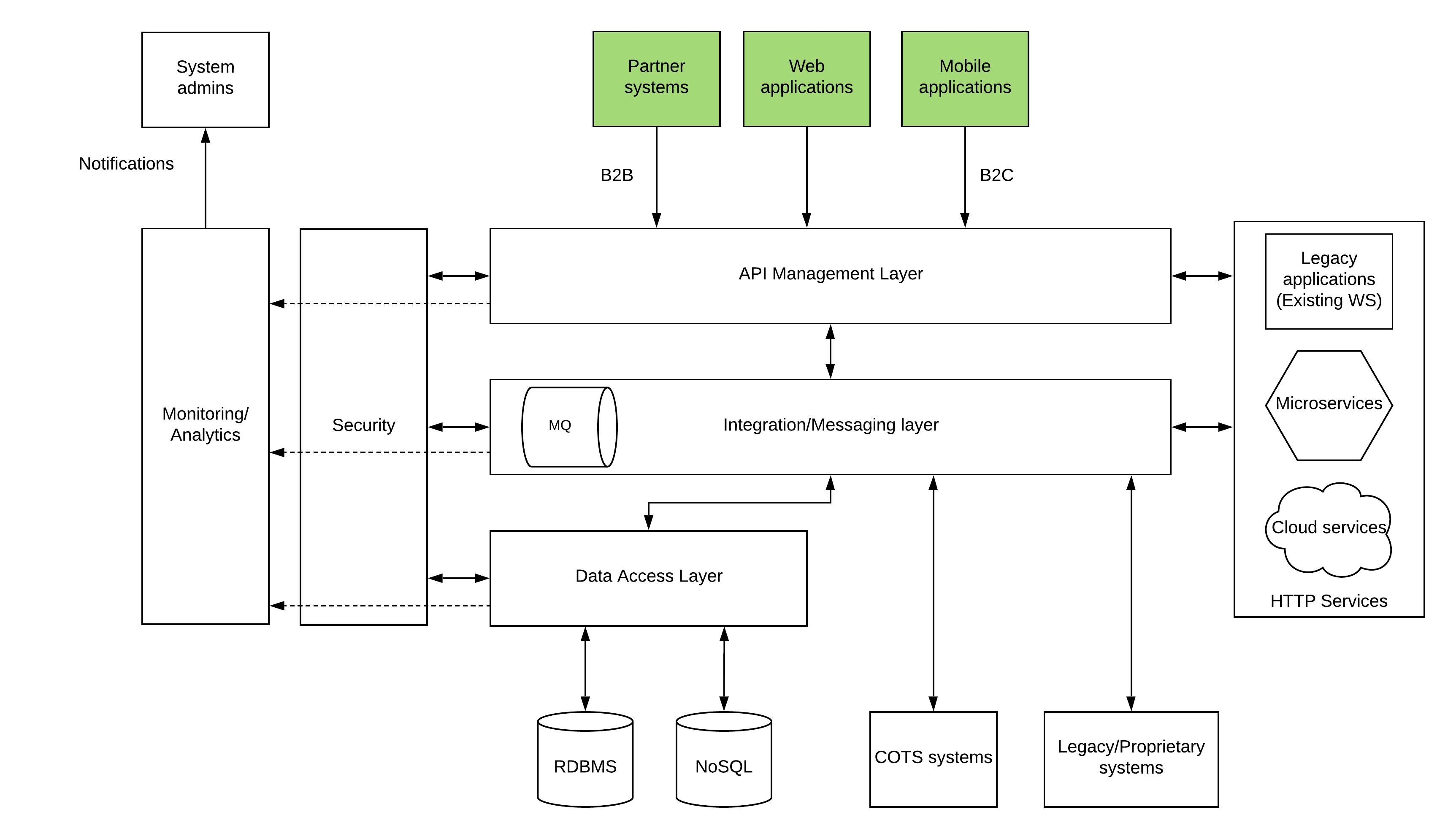
Data Access Layer
As depicted in the above picture, core system which is providing the data which is stored in databases is built through the data access layer. This layer will make sure that data is accessible over a more systematic mechanism like SOAP or REST by converting the complexities of database connection handling and transactional behaviours.
Integration Layer
Your enterprise systems are built throughout a longer period of time and there can be many different systems which has been playing key parts in your enterprise system. These disparate systems needs to be interconnected in a manner that those systems does not need to be modified to understand the connecting systems. That is the task of an integration layer which interconnects systems which are communicating over different protocols, messaging formats.
API Management Layer
Exposing your business data through various consumer channels like mobile, web and other means is critical in providing an unmatching customer experience. API Management layer controls all the channels which exposes data to external and internal users and apply measures like security, throttling and monitoring so that every business transaction means something to the end user as well as the business.
Web services Layer
If your organization is somewhat ahead of time thinking and going with the bleeding edge technology, you could have ended up having some amount of your business data in cloud services, micro services or some type of HTTP services layer. This layer can be connected into either Integration Layer or API Management Layer which will eventually connect with the end users.
Security
Data security is not an afterthought anymore. Valuable business data and transactions needs to be properly secured and authentication and authorization of data access will be crucial in enterprise system design.
Monitoring and Analytics
At the end of the day, your business leaders need to grow your business each day and as system designers you should enable necessary capabilities through your design. Monitoring and analysis of business transactions is crucial in identifying the business and user trends within your platform as well as across the business domain.